END USES
Wind energy can be used for a variety of applications and, in many cases, it can serve as a substitute for conventionally produced electricity. There are different sized turbines that are used for different applications and the size of the turbine correlates with the amount of energy needed for a designated application. Wind turbines are used to generate wind energy for residential-scale onsite energy use, small commercial-scale onsite energy use, commercial onsite energy use, large commercial or industrial energy use, or even utility-scale energy use. Wind turbines of all sizes convert the kinetic energy in the wind into mechanical power. This power can then be used for specific tasks or it can be converted into electricity using a generator.
According to the Energy Information Administration (EIA), about 4,116 billion kilowatthours (kWh) (or about 4.12 trillion kWh) of electricity were generated at utility-scale electricity generation facilities in the United States in 2021. About 19% was from nuclear energy, and about 20% was from renewable energy sources. Wind accounted for 9.2%. About 61% of this electricity generation was from fossil fuels—coal, natural gas, petroleum, and other gases.[1]
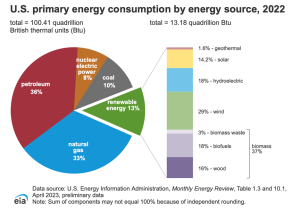
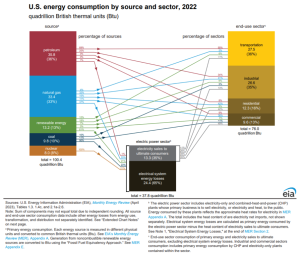
According to EIA, the total U.S. primary energy consumption in 2022 was equal to 100.41 quadrillion Btu, of which renewable energy supplied 13.18 quadrillion Btu, or 13%. Wind accounted for 29% of the total renewable energy consumed. [2]
Wind energy in the U.S. is almost entirely used by wind-powered turbines to generate electricity in the electric power sector.[3] As of quarter 1 2023, the total installed wind capacity was 145,569 MW.[4]
Updated January 2024 by Jennifer Ostromecki

Comments are closed.